Hard Drive Glossary
Access
Access refers to the process of retrieving data from or writing data to a data storage device.
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is an organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus standards for various industries in the United States.
ATA
Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) is a standard interface for connecting storage devices like hard drives to computer systems. Originally designed for embedded fixed-disk storage on IBM AT-compatible PCs, ATA has become the dominant storage interface.
Bit
A bit is a binary digit, which is the basic data unit for digital computers. It can only contain the value 1 or 0.
Buffer
A buffer is a temporary storage area used to compensate for differences in data transfer or processing rates between sender and receiver.
Byte
A byte is a unit of digital information consisting of eight bits.
Cache
A cache is a small, fast memory area (usually DRAM) on the hard drive used to store temporary data that has recently been accessed or is awaiting writing to the disk.
Capacity
Capacity refers to the amount of data that can be stored in a given storage device, usually expressed in bytes.
Channel
A channel, in the context of a data cable, is a collection of electronic circuits that facilitate data writing and reading processes to and from magnetic media.
Data
Data is an organized collection of information.
Gigabyte (GB)
A gigabyte (GB) is a unit of storage. In the decimal system, 1 GB is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes, while in the binary system, it equals 1,073,741,824 bytes. Hard drive manufacturers typically use the decimal system, while operating systems use the binary system, leading to discrepancies in reported hard drive capacities.
Jumper
Jumpers are used to set a hard drive’s attributes, such as Master/Slave. They act as simple on/off switches, connecting two pins to close a circuit. Different combinations of jumpers result in different settings.
Latency
Latency refers to the delay between making a request and receiving the corresponding response. Lower latency is preferable.
Megabyte (MB)
A megabyte (MB) is a unit of storage. In the decimal system, 1 MB equals 1,000,000 bytes, while in the binary system, it equals 1,048,576 bytes. Hard drive manufacturers and operating systems use different systems for calculating storage capacity, which can lead to discrepancies.
PATA (Parallel ATA), IDE/EIDE (Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics)
PATA, or Parallel ATA, is an older hard drive interface standard that uses a 16-bit parallel connection to link storage devices and motherboards. It is also known as IDE or EIDE (Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics). Two popular PATA standards are ATA-6 (also known as Ultra ATA 100 or Ultra DMA 100) and ATA-133, with maximum bandwidths of 100 MB/s and 133 MB/s, respectively.
SATA (Serial ATA)
Serial ATA (SATA) is a hard drive interface standard that uses serial signaling technology to connect storage devices to computer systems. SATA offers several advantages over PATA, including longer, thinner cables for better airflow within computer chassis, fewer pin conductors for reduced electromagnetic interference, and lower signal voltage for minimized noise margin. SATA also provides greater bandwidth, with SATA 1.0 reaching 1.5 Gb/s (150 MB/s) and SATA 2.5 supporting up to 3 Gb/s (300 MB/s).
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
SCSI is a standard interface for transferring data between devices and computers. Its ability to compartmentalize diverse operations makes SCSI well-suited for multitasking operating environments. When multiple devices are connected, SCSI
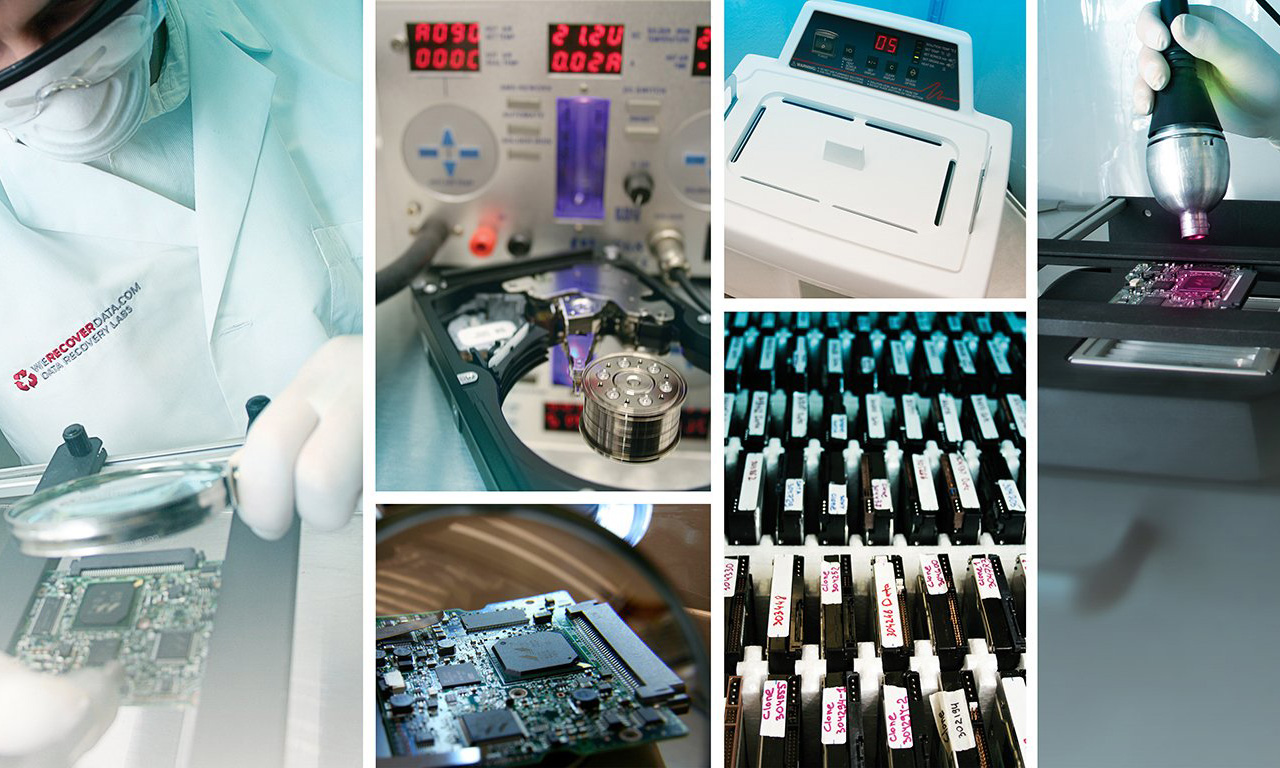





















Great company!
I think it is the best company in the world regarding data recovery. They take all types of recovery cases with great responsibility and ensure they work with the best possible solution for your specific case. I highly recommend it.
Superb effort
Superb effort from werecoverdata. I had no idea how to fix it when I faced a horrible problem with my RAID NAS. But they solved it very quickly and superbly. I recommend them!
Fantastic results
Thanks to all staff of werecoverdata for excellent work and for getting my company data back! I got frustrated when a deadly drop damaged my hard drive. But they solved it!
Thanks
Few days ago my raid server is crashed dangerously. It was not starting any more. I tried in a various way whatever I know but I could not fix it. My uncle told me about WeRecoverdata. Then contact with them and they repaired it. Thank you guys.
Recover service
Those are suffering bad experience of getting a reliable and professional recovery service provider, definitely, they can choose werecoverdata. I highly recommend it.
Thanks a lot
The location is a bit hard to find out but eventually, I did. They recovered my hard drive, which was mostly dead. Thanks a lot.
Great response
Definitely weRecover team is great to solve that kind of hard drive problem. Great response and remarkable. They recovered my all data successfully within short time. I wanna give special thank to David. Thanks a lot man.
Liked Your Service
I have been using my HP laptop since 2016. Few months ago I could not open my laptop. After pressing the power button its showing nothing. My friend told me about that company. They recovered my laptop. Now its working perfectly. Thanks a lot WeRecoverData.
Pretty good experience
It was really pretty good experience. They are so professional, punctual and reliable. I strongly recommend it.
Remarkable Work
A lot of thanks to werecoverdata. You did really remarkable work. I was frustrated when lost my important data from a hard drive. I sent my hard drive to WRD then they got all the data back. At first, I couldn’t believe anyone can recover it since my computer tech said he can’t do it. All credit goes to werecoverdata.
Gorgeous service
Fantastic service from all the guys at werecoverdata. I was having pressure when corrupted data from my hard drive .Then I went there and they fixed it superbly.Thanks for removing the pressure!
Extremely well
I faced horrible problem but they solved it extremely well.My problem was that hard drive crashed dangerously.At this moment I thought the sky was broken on my head.Thank you for that.
Sensible
Thanks to WeRecoverData. You fixed the hard drive problem promptly. I am impressed… Anybody can rely on werecoverdata.
Well done
Thank you
Great work
Obviously great work from werecoverdata.Definitely no doubt about this company because they take seriously to solve any kinds of problem.I have lot of assurance at them.A lot of thanks to them.
Fantastic work
Oh Tom really fantastic work. You saved my important days. Raid 5 server damaged dangerously few days ago. But you fixed it well. Thank you for that!
Great efforts
All credits goes to werecoverdata for recovering raid server.I thought impossible to repair it but they was taken sensible and fixed it.Now I can fully trust on werecoverdata.All thanks to them.
Helpful Work
Werecoverdata, you did a really very helpful work.I was angry when my hard drive got dropped from my mistakes. I recommend the company and give a lot of thanks to werecoverdata.
Best service
After my hard drive crashed I was going to be totally mad. One of mu cousin suggested me to meet that company. I did and got the best service ever I had.
Remarkable Job
AWESOME service from WeRecoverData. I was almost mad when my pc crashed. A lot of valuable data in my hard drive. One of my friend recommend it. I thought it will not be possible.
But after all I got back my all data. Thank You WeRecoverData.